 |
| I've covered this topic on my cruise ship presentations on coffee. |
Caffeine is the most widely consumed psycho-active substance in the world!
Caffeine is not the work of Satan, nor the product of some mad scientists working in a chemistry lab; rather, it’s the result of millions of years of plant evolution.
All plants build a variety of compounds including enzymes. Many of these molecules serve as a defense against enemies of the plants—large and small.
Building caffeine is an expensive process (energy-wise) for the plant, so why do they do it?
For coffee, the most widely consumed and widely studied caffeinated plant, there are 3 reasons that we know about.
1) The caffeine in fallen leaves acts as a mild herbicide, which discourages weeds around the plant.
2) The bitterness of caffeine discourages bugs and other herbivores from eating the leaves.
3) There is caffeine in all parts of the plant, including the pollen & nectar so the pollinators, mostly bees, receive a little bit of a buzz, so to speak, and this makes them better remember the source. (This
always gets a laugh in my presentations.)
Read Arizona State University article: "Bees get a buzz from caffeine found naturally in flower nectar."
There are other plants around the world that produce caffeine, as well
Only a few plants in different plant families in various parts of the world produce caffeine. Isn't interesting that somehow even the earliest humans figured out which ones they were?
 |
| Cup of coffee |
Coffee
Coffee is in the gardenia family (Rubiaceae). There are two species of coffee that are widely consumed: Arabica coffee (Coffea arabica) and Robusta coffee (C. canephora var. robusta). They are both native to Sub-Saharan Africa. The robusta coffee has about twice as much caffeine as arabica and makes up about 40% of the market share and nearly all of the instant coffee. Partly because of its higher caffeine content, it's easier to grow requiring fewer pesticides than arabica amd it can be grown in more places. Arabica coffee does best at higher altitudes, while robusta can grow at sea level. It is, in fact, more robust.
 |
| Florida native, yaupon holly, produces caffeine. |
Yaupon holly
Yaupon holly (Ilex vomitoria) is native from Virginia to Texas, Cuba, and the Yucatán Peninsula. It's in the holly family, Aquifoliaceae. Several cultivars are widely planted as foundation plants in Florida and it's commonly found in the native plant trade. Here's its profile on the Florida Native Plant Society website, which includes a link of vendors that have it for sale. As the only caffeinated plant in the country, it has an interesting history. "The indigenous Timucua people of Florida called Yaupon Cassina, and believed that it purified the mind and body of those who drank it." Yaupon Brothers have built a business producing this American tea.
Yerba mate: another holly with caffeine
Yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) is native to eastern South America south of the Amazon River. Indigenous peoples in the region were already drinking it by the time the Europeans arrived. Plantations were established to grow it commercially and since the male* holly plants produce more caffeine, most of the planted trees were male to produce a stronger drink. The volume of mate for the infusion is much greater than other teas. *Hollies are dioecious plants, meaning male and female flowers are located on separate plants. Female plants produce the fruit.
 |
| The source of chocolate. |
Cacao or cocoa tree
Cacao or cocoa tree (Theobroma cacao) is in the mallow family, Malvaceae, so it's related to hibiscus and the various mallows. It's native to northern South America including the Amazon Basin. Its large fruits grow directly on the trunk of the tree and the seeds, which are not beans, contain caffeine. Note since the caffeine is water soluble and is contained in the dark cocoa once the seeds have been processed, so white chocolate made from the cocoa fat has no caffeine. Again, indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica and South America were drinking caffeinated cocoa drinks well before the Europeans arrived.
 |
| The Chinese have been drinking tea for millennia. |
Chinese tea
Tea (Camellia sinensis) is a species of evergreen shrub or small tree in the flowering plant family Theaceae.
The longest “recorded history” of caffeinated drink comes from China where they made tea using tea leaves from this camellia shrub more than 4,000 years ago, but they were probably drinking it long before then.
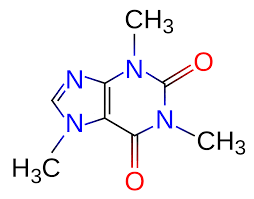 |
| Caffeine is a complex molecule. |
Caffeine
Plant physiologists studied how coffee and tea—unrelated plants—produce caffeine and discovered that it’s produced with a different set of enzymes and goes through an entirely different chemical pathway to produce the very same caffeine molecule.
Caffeine is so beneficial that both plants evolved different ways to produce the very same molecule. When this happens we call it Convergent Evolution.
As far as its effect on humans, it's a stimulant and even the earliest peoples were aware of this. Now caffeine is the basis for many industries, including growing caffeine-producing crops, and then both processing it for consumption and removing it from products so people can cosume those products without all that stimulation.
As gardeners and biologists, plants form the basis for our very existence. Through photosynthesis they remove carbon dioxide from the air, produce sugars which is in all of our food, and produce oxygen, which we breathe. For more details on this, I discussed the three cycles in plants (water, carbon, & oxygen) in this article.
Plants produce caffeine, which keeps people alert so we can accomplish more in our day-to-day lives. So, have you thanked a plant today?
Green Gardening Matters,
Ginny Stibolt



Great article...Hadn't thought of caffeine as an herbicide.
ReplyDelete